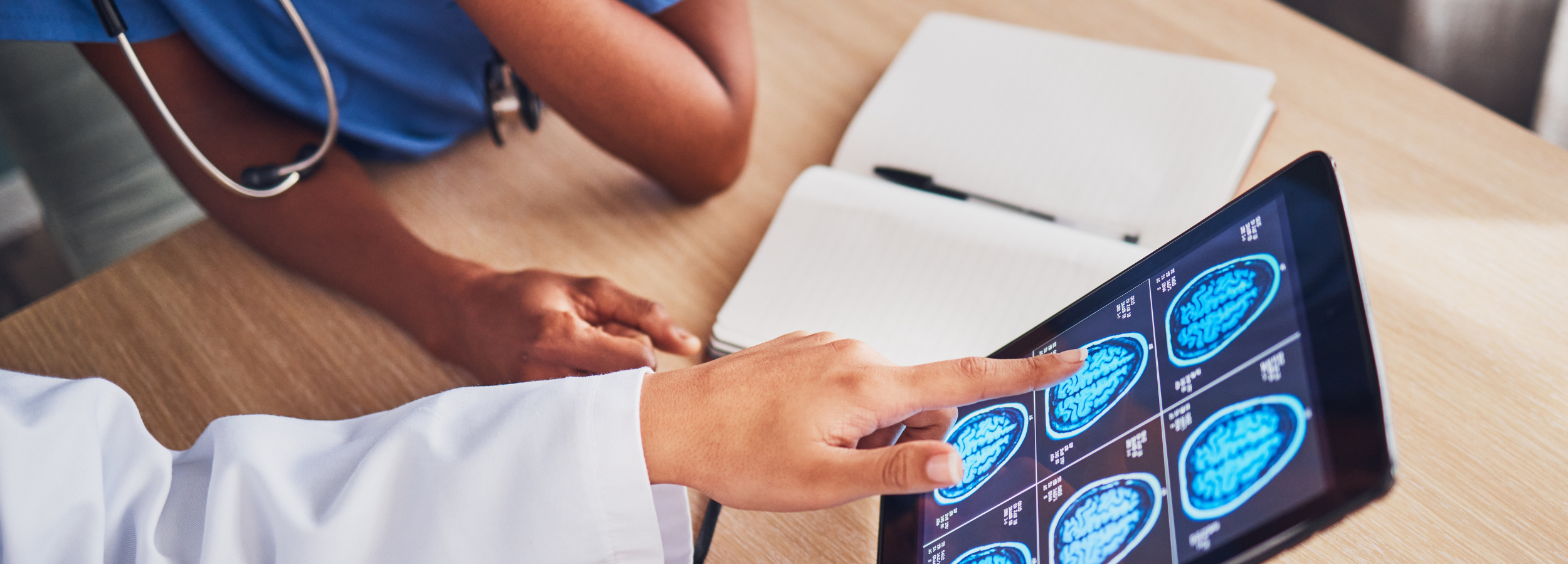
Supporting Cognitive & Neurological Longevity
Neurological changes often develop gradually. Early indicators of cognitive decline, nerve damage, or structural abnormalities can go unnoticed until symptoms become more pronounced.
Proactive brain health testing helps you:
- Understand structural changes within the brain
- Identify early signs of neurodegeneration
- Evaluate nerve and muscle function
- Support timely diagnosis of neurological abnormalities
- Detect biomarkers linked to long-term cognitive conditions
- Gain clarity on symptoms such as memory loss, numbness, weakness, or coordination changes
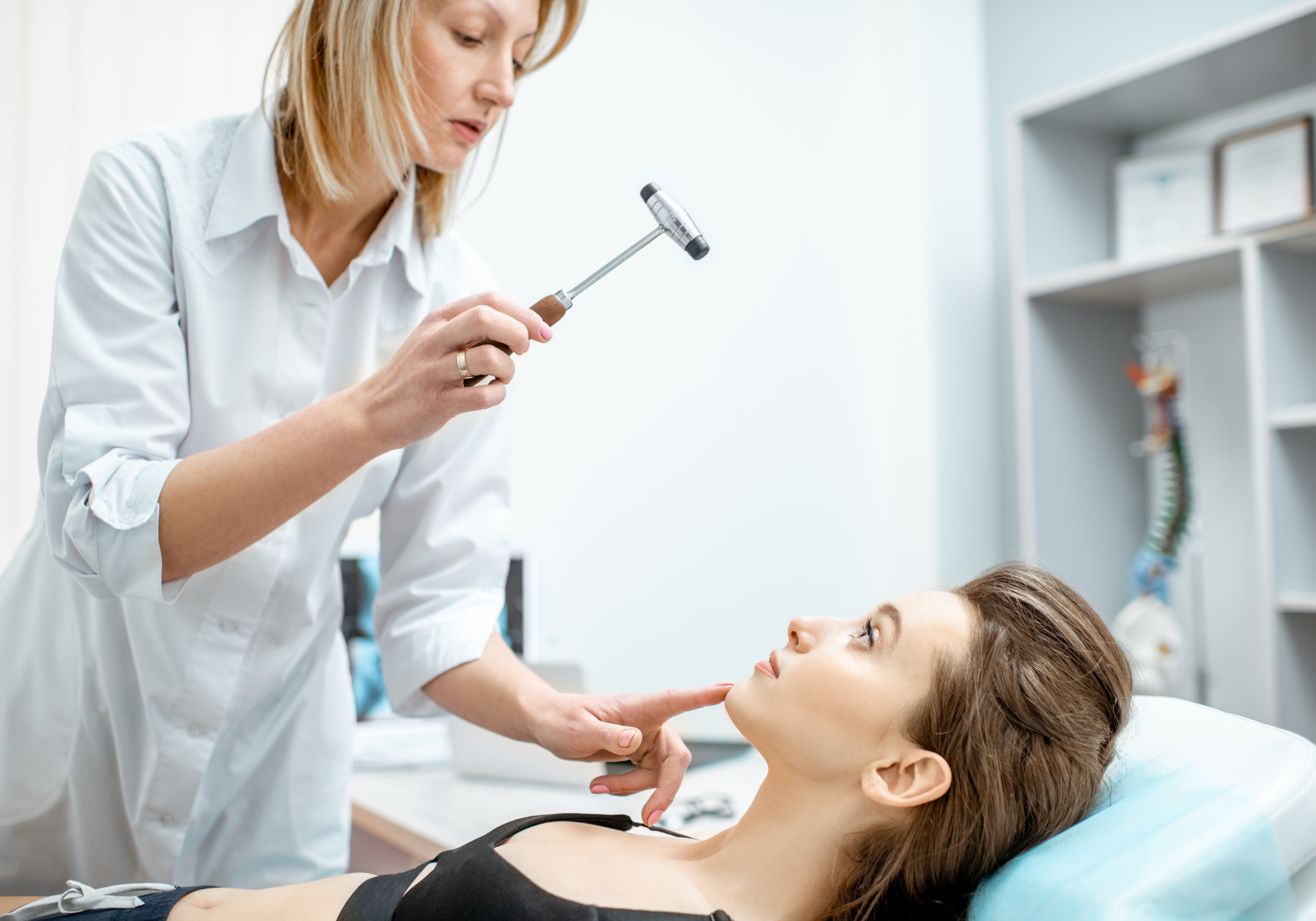
Neurological Functional Assessments
A hands-on evaluation of brain and nerve function.
This includes a complete Neurological Examination: Assesses reflexes, balance, coordination, muscle strength, sensory function, and motor responses.
Provides a holistic view of brain-body communication and potential areas of impairment.
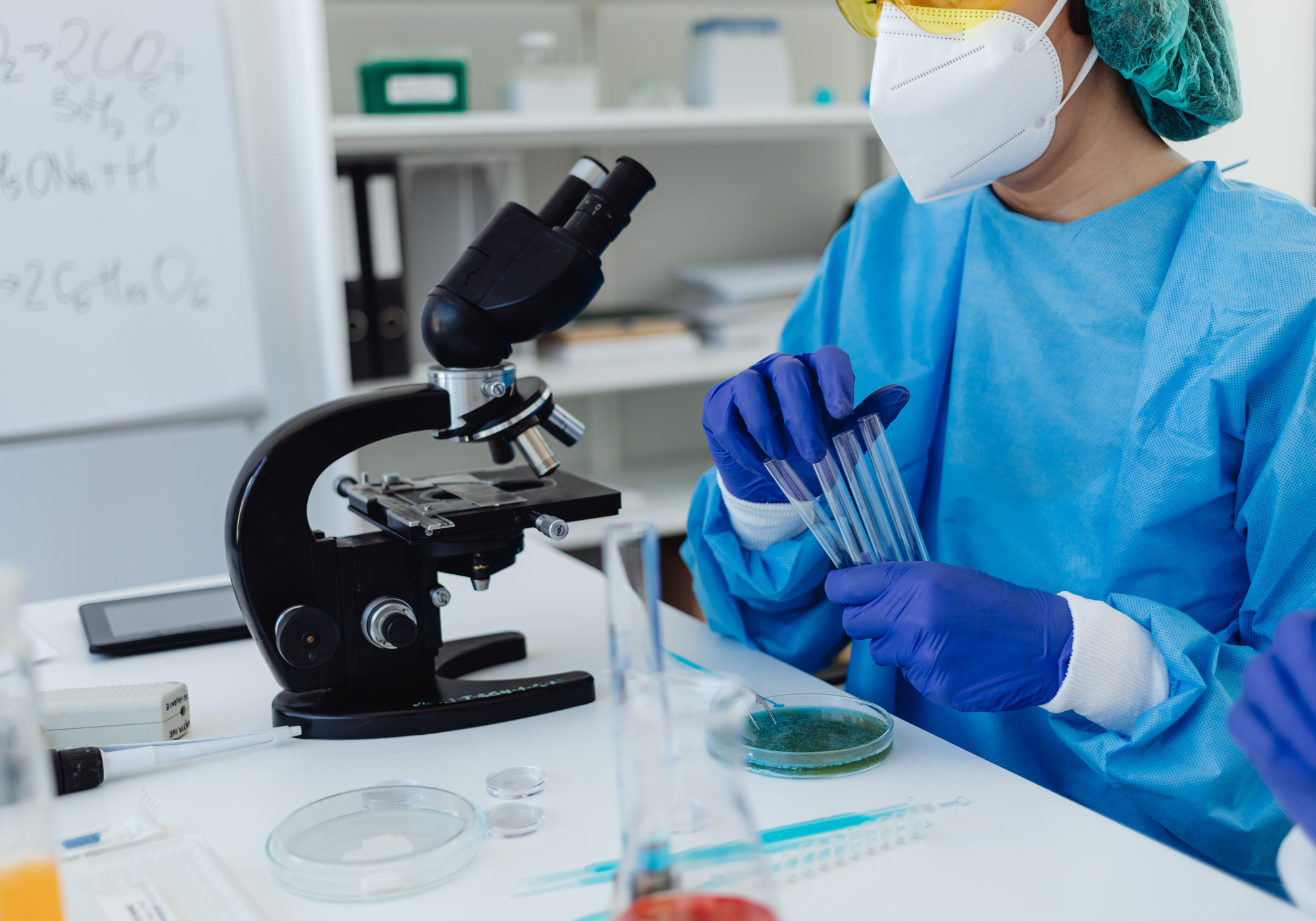

Laboratory Markers for Brain Health
Blood and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) tests can provide valuable insight into inflammation, infection, and neurological biomarkers.
Tests Included:
- Blood Biomarker Testing: Screens for markers associated with inflammation, autoimmunity, infections, or metabolic contributors to neurological symptoms.
- CSF Analysis (Cerebrospinal Fluid Test): Can detect biomarkers used in the assessment of certain neurological conditions (performed when clinically indicated).

Cognitive Function Tests
Validated, pen-and-paper or clinician-administered tests designed to evaluate multiple domains of cognitive function. They assess Memory (immediate & delayed recall), Attention & concentration, Orientation, Language & fluency, Executive function, and Visuospatial skills.
Tests include:
- Addenbrooke’s Cognitive Examination (ACE-III): A comprehensive and widely respected cognitive assessment for early screening of conditions such as dementia, mild cognitive impairment, and other neurological disorders.
- GPCOG (General Practitioner Assessment of Cognition): A fast, effective screening tool commonly used in primary care for initial cognitive screening, helpful in identifying early signs of impairment, and offering a quick yet structured assessment for memory and thinking concerns.
- Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA): One of the most widely used tools in early cognitive screening. MoCA is particularly sensitive to detecting early cognitive decline that might not appear on shorter assessments.
How It Works
Step 1: Initial Consultation
Discuss your symptoms, concerns, cognitive changes, headaches, nerve issues, or family history of neurological conditions. Your consultant selects the most appropriate tests for your needs.
Step 2: In-Clinic Testing & Imaging
Neurological examinations, blood work, electrophysiological tests, and imaging referrals (MRI, CT, PET) are arranged through accredited facilities.
STEP 3: Specialist Interpretation
All findings are reviewed by clinicians trained in neurological assessment. Imaging results are interpreted by expert radiologists.
Step 4: Personalised Plan
Your consultant provides a detailed explanation of your results with clear next steps, which may include lifestyle adjustments, targeted treatments, or referral to a neurologist if necessary.
Ready to understand your brain and cognitive health more deeply?
A practitioner consultation is mandatory before scheduling diagnostics.
Disclaimer
These tests provide insights into neurological health and may support timely diagnosis when abnormalities are detected. They do not replace urgent medical evaluation. If severe symptoms occur (such as sudden weakness, speech difficulty, or loss of consciousness), please seek emergency care immediately.


